Efficient cooling is crucial, in systems to ensure they operate reliably and maintain performance while also prolonging the lifespan of components as devices become smaller and more powerful managing heat from processors and GPUs is a key factor, in design considerations.
Efficient temperature regulation requires more, than getting rid of heat; it also entails finding a way to maintain a harmony between energy efficiency noise levels and costs involved in the process. This equilibrium is vital in devices like computers and industrial machinery and relies heavily upon sophisticated cooling techniques, like dynamic fan control.
The use of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) cables is crucial, for controlling fans in todays systems to ensure optimal cooling performance based on temperature changes in real time. The advancements in PWM technology allow for cooling effectiveness along with quieter fan operations. Improved energy usage management within electronic devices. This discussion emphasizes the importance of cooling systems in electronics and highlights how PWM cables play a role, in maintaining thermal control.

What is PWM
PWM is a method utilized for regulating power distribution to gadgets by turning the power source on and, off. The term “modulation” involves modifying the duration of the “on” pulses in comparison, to the “off” pulses during a time frame .This proportion referred to as the duty cycle decides the power sent to the device linked to it.
- Understanding the Functioning of PWM
- PWM functions, by alternating a power signal from power (100 percent voltage) to zero power (no voltage) at a rate. The secret, to controlling the power output depends on the duty cycle;
- Having a duty cycle (for example 75%) implies that the signal remains active for a portion of each cycle which leads to an increase, in power consumption.
- Lowering the duty cycle to, around 25% decreases the duration of operation and results, in reduced power output.
Cooling fans use PWM for speed control by adjusting the power input to the motor neatly spinning it faster when the duty cycle is raised to remove heat efficiently and slowing it down when the duty cycle decreases to conserve energy and lower noise levels.
- PWM ensures that the entire voltage is maintained during the “, on” pulses to minimize energy loss in contrast, to voltage regulation methods that could result in energy wastage through heat dissipation.
- When it comes to fan speed control PWM stands out for its consistent performance especially when operating at speeds.
- Reducing Noise Levels; Voltage control may lead to motor noise when operating at speeds; however Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) provides a performance.
- Modern fan motors are designed to work with PWM signals. This approach is becoming more common nowadays.

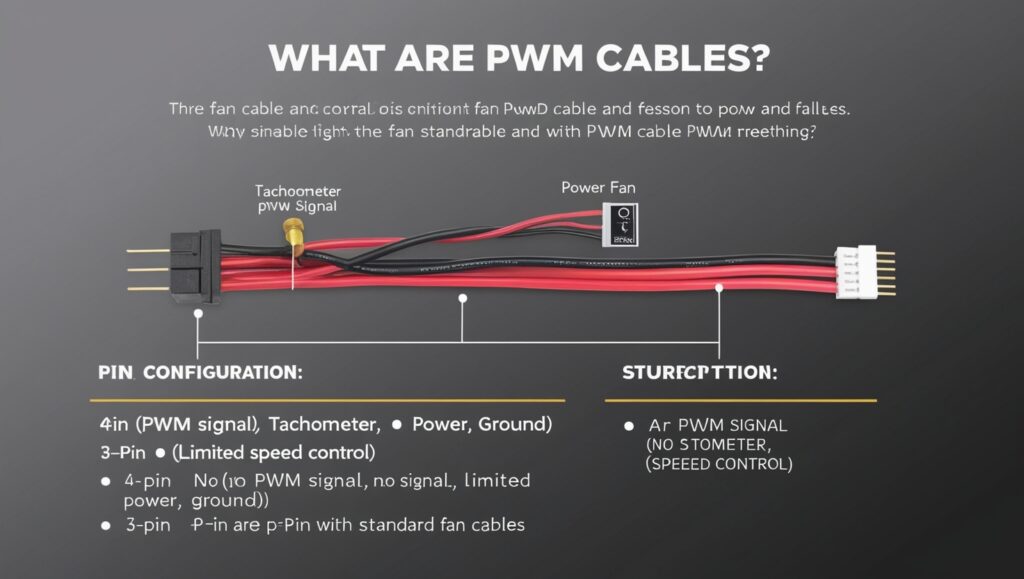
What Are PWM Cables
PWM cables are custom connectors utilized in cooling setups to adjust fan speeds. They send signals that allow control, over how a fan operates to maintain notch cooling effectiveness and energy conservation. The cables serve as a link, between a systems motherboard or fan controller and the cooling fan.
- Arrangement of PWM Cable Pins.
- A cable, with four pins, for PWM connection.
Pin 1 (Ground) This pin establishes a shared ground connection, for the circuit.
- Pin 2 provides a +12 volts of DC power to operate the fan motor.
- Pin number 3 known as the tachometer sends a signal that keeps track of the fans speed in rotations, per minute (rpm).
Pin 4 (PWM Signal) This pin transmits the PWM control signal that adjusts fan speed by modifying the duty cycle.
- The 4 pin configuration is commonly used in todays PWM fans to provide speed regulation while ensuring consistent power supply.
Three-pin fan cable ( without PWM)
- Pin 1 (Ground); This serves as the shared ground connection, for the circuit.
- Pin 2 labeled as “Power ” supplies voltage (usually ranging from 5 to 12 volts DC) allowing for the control of fan speed.
- Pin 3 of the device functions, as the tachometer providing the motherboard or controller with information regarding the fan’s speed in revolutions, per minute (rpm).
- In three-pin fans speed adjustments are made by changing the voltage sent to the fan motor. This method doesn’t offer the control of PWM regulation.
Role of PWM Cables in Fan Control
PWM technology provides benefits, for controlling cooling systems by ensuring that fans run efficiently and effectively to maintain peak performance and comfort levels. Benefits of PWM Fan Control
Achieving control, over the fan speed
PWM fans provide control over fan speeds by adjusting the PWM signal’s duty cycle, allowing for regulation and optimal performance. Fans can spin at speeds ranging from low to maximum RPM without experiencing stalling or compromising reliability. The enhanced ability to adjust to variations in temperature demands enables the fan to promptly cater to the cooling requirements of the system.
Balancing the effectiveness of cooling
PWM technology allows for an equilibrium, between cooling effectiveness and noise levels. When parts produce heat (such, as when they’re not in use or under light load) the PWM signal is used to lower the fan speed, for quieter performance and reduced energy usage. When there is a lot of work going on and things start heating up the fans kick into gear to keep everything cool and avoid any overheating issues.
This flexibility guarantees that fans run intensively as needed to prevent the continuous loud noise typical of conventional fixed-speed fans.
Utilizing Temperature Sensors
PWM fans function smoothly alongside temperature sensors that are built into the motherboard or other system components resulting in a collaboration that offers; The fan speed adjusts, in time to changes, in temperature to make sure heat is efficiently dispersed when required.
Certain cooling systems offer the capability to monitor temperatures, in zones which helps fans to efficiently cool particular areas. Efficiency, in energy usage is improved by adjusting the operation of the fan based on conditions, through PWM technology to reduce unnecessary power consumption and prolong the lifespan of both the fan and components.
In summary
PWM fan control stands out as a crucial feature owing to its precise regulation abilities coupled with reduced noise levels and dynamic cooling functions that enhance user experience in a seamless manner.

Applications of PWM Fans and Cables
Common Use Cases for PWM Fan Control
PWM-regulated fans are extensively utilized in a variety of applications due, to their effectiveness and accuracy, and ability to adapt to scenarios. Here are a few examples of the situations where they are commonly employed;
- Cooling systems, for processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs).
- Today processors and graphics cards produce a lot of heat when handling demanding tasks such, as gaming or video editing due, to their design features and capabilities.
Advantages of PWM
- Fans are smartly tuned to ramp up their speed when handling tasks and ease off when there is not much going on to keep things quieter and save on power usage.
- Helps to avoid heat while ensuring that it operates quietly when not under heavy load situations.
- Servers need to run all the time with workloads and temperatures to make sure they stay reliable and operational consistently.
Advantages of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- Provides an adjustment for regulating cooling in densely packed server racks.
- Decreases the amount of energy used in data centers by addressing the power consumption caused by fans.
- Reduces disturbances in places where servers are housed alongside employees.
- Server motherboards usually have PWM headers to manage fans based on system temperatures, in real time.
- Cooling systems, for factories and industries.
- Machinery, in settings frequently encounters challenging conditions, with varying temperatures and PWM fans offer cooling solutions customized to meet specific operational requirements.
- Their ability to adapt and manage efficiently ensures that the equipment remains at peak performance and lasts longer when subjected to use.
Pushing the limits
- Push the components to their limits through overclocking. You’ll see a jump, in the heat they kick out.
- PWM fans play a role, in keeping temperatures stable and avoiding throttling or potential damage.
- Fans controlled by PWM are frequently combined with cooling systems such, as coolers to achieve peak performance levels.
PWM fan control has become essential, for maintaining temperature levels in CPUs and GPUs under workload situations as well as in regulating heat in servers and industrial setups where there are unique thermal requirements to address efficiently and effectively while ensuring a balance, between performance effectiveness and noise reduction is maintained.
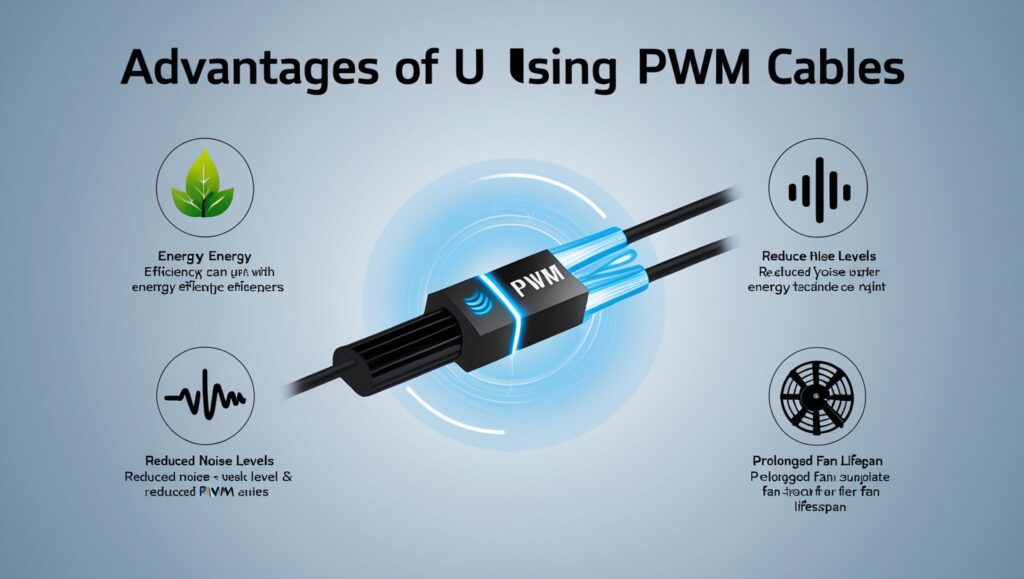
Advantages of Using PWM Cables

The Benefits of Using PWM for Fan Control
PWM technology provides advantages for cooling systems. Is often the top choice, for modern thermal management needs. Here are three key benefits
- Improved Energy Efficiency
- PWM fans work with speed control. Adjust dynamically to meet the cooling needs of the system.
- They conserve energy by running at the speed to match the task at hand and avoid unnecessary exertion during times of low activity or minimal use, like when the system is idle or running light applications.
- The fluctuating pattern of PWM signals helps to keep a voltage supply that reduces power wastage in comparison, to fans controlled by voltage which release power as heat.
- Using energy efficiently helps save power. Is particularly beneficial, in places such as data centers or offices with many systems, in place.
- One great advantage of PWM control is its capability, in minimizing noise disturbances.
- During times when there is need, for cooling or heating in a room or space fans run quietly as they are set to lower speeds making them much quieter compared to fans that run at a constant speed.
- The gradual shifts, in speed settings of fans controlled by PWM help avoid noisy fluctuations in fan rotations, per minute (RPM).
- Operating quietly is particularly advantageous, in consumer gadgets and workplaces that appreciate silence – such, as recording studios or living spaces.
- Increasing the longevity of fans
- The efficiency of operations has an influence, on how cooling fans last.
- When PWM fans run at speeds in situations where cooling power is not required they undergo less strain, on their bearings and motors.
- Minimizing stress and reducing heat exposure can help prolong the lifespan of the fans.
- Making substitutions helps cut expenses and lessens electronic waste in line, with eco approaches.
PWM fan control is a technology, in cooling solutions as it offers a blend of efficiency and quiet performance while ensuring durability for long-term use benefits, to both users and system design efficiency.
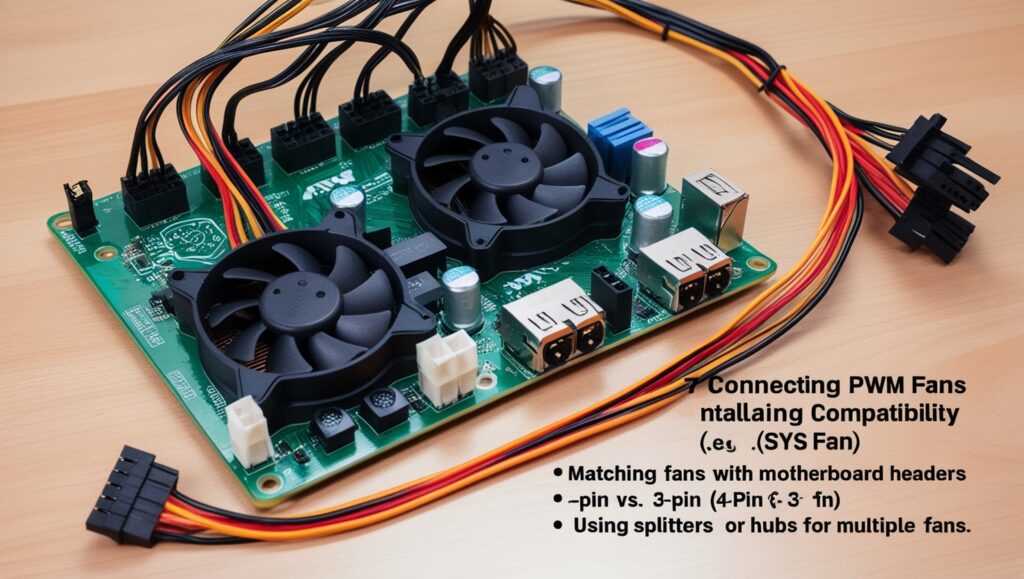
Installation and Compatibility
How to Link PWM Fans to Motherboard Ports
Ensuring that PWM fans are correctly connected to the motherboard headers is important, for maximizing cooling efficiency and effective fan management.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to set up PWM fans
Establishing a connection, with the motherboard headers.
The header for the CPU fan
- Usually used for the cooling fan. Pump in the CPU cooler.
- The BIOS keeps an eye on this headline and alerts or shuts, down the system, in case of fan failure.
- Make sure to employ a 4-pin PWM fan, for optimal speed adjustment linked to the CPU temperature.
SYS FAN Headings
- Ideal, for enthusiasts looking to enhance airflow or incorporate cooling components.
- There could be headers, in the BIOS or software settings that can be adjusted individually.
- These headers allow PWM fans to adjust based on system or GPU temperatures.
The header, for the AIO_PUMP (if provided)
- Designed for water cooling pump setups. Can also accommodate PWM fans, for power supply as required.
Comparing 3-Pin Fans to 1-Pin PWM Technology
- Fully compatible, with 5-pin motherboard headers. Ensures speed control through the PWM signal, for the performance of your fans.
Using 4-pin headers for 4-pin connectors
- It will work. Only, with voltage-based control and not, with a PWM signal.
- The accuracy of speed adjustments may not be as exact. The fan might not work well at speeds.
- Fans, with 3 pins can be connected to headers with 3 pins.
- The fan will run at speed since there is no PWM signal pin, for control.
Inspecting the specs of the motherboard
- Make sure that the motherboard has PWM control support, for all connectors where you need control as some connectors may only offer voltage-based control.
- Utilizing Splitters or Fan Hubs
- Fan splitters are a tool, for dividing the airflow in a room to ensure circulation and distribution of cool air.
- Enable the option for several fans to share one header.
- Usually, the PWM signal is distributed to all the fans that are linked together so that they run at speeds.
- A single fan typically sends the RPM signal to the motherboard because each header can only read one tachometer signal at a time.
Enthusiast Centers
- Fan hubs are a step up, from splitters as they not only deliver power from the PSU but also transmit signals, for control from the motherboard.
- Ideal, for systems, with fans as they help avoid putting much strain on motherboard connectors.
Factors to take into account when thinking about power
Make sure not to exceed the power limit of each motherboard header (usually around 1 ampere (1 A) and 12 watts (12 w)). Be cautious of the power consumption, from all connected fans when using splitters to avoid going over this threshold.
To set up PWM fans correctly on your motherboard requires knowledge of header types and power constraints to ensure they work well for cooling and system performance. Whether you’re using a fan or a setup, with splitters or hubs, for fans while aiming for efficient cooling and quiet operation.
Maintaining and Upgrading PWM Systems
Guidelines, for Keeping Your System in Top Shape
For performance and durability of your cooling system, in the run here are some maintenance suggestions to keep in mind
- Routine Maintenance
Getting rid of dust
- Dust buildup, on fans and filters can lower cooling performance over time; it is recommended to use compressed air to clean these components every 3 to 5 months, for efficiency.
- Blades, for fans.
- Make sure to clean the fan blades to avoid dust accumulation, which could lead to the fan becoming unbalanced and causing noise or vibrations.
Verify if the fan is functioning properly
- Check the fans for any sounds or wobbling movements and variations, in speed that could signal wear and tear or damage.
- Make sure all the fans are rotating when you turn the system On because a fan that isn’t spinning might need to be replaced reconnected, checked out, and fixed up properly for things to run smoothly.
- Utilize system monitoring programs, like HWM monitor or Speed Fan to keep an eye on the temperatures of your CPU, GPU, and computer case.
- The cooling system is not working effectively.
- Components often become too hot. This can lead to issues, like throttling or unexpected shutdown events.
- Your existing setup relies on voltage-controlled fans with three pins that struggle to maintain speeds; this often results in operation or less, than optimal cooling efficiency.
- The equipment is getting old.
- Signs of wear, on fans or other components may include noises from the bearings and irregular operation, like wobbling.
- The motherboard doesn’t have PWM headers which makes it challenging to connect fans or high-performance ones.
- The rising levels of ambient noise
- Fans constantly run at speeds because they lack control which leads to them making too much noise.
- The acoustic characteristics of your system may impact the ambiance of your workspace or living space.
- You’ve installed parts, like CPUs or GPUs that produce more heat than your current cooling system can handle.
- When you’re using your system for tasks, like overclocking or other demanding activities it’s important to have cooling to ensure performance.
- In systems that are always running such as servers or workstations, it is important to decrease power usage and minimize noise levels without compromising on cooling solutions, for performance and reliability.
Keeping your system clean and well-tuned can help extend the life of your components and maintain performance over time. If you’re facing issues, with your system not handling today’s demands or if it’s getting too loud and ineffective consider investing in cooling solutions that are compatible with PWM, for better results.
- If the temperature goes beyond check the airflow, fan velocity, and how the thermal paste is applied.
- Fine-tune the fan settings, in your BIOS or control software to find the balance, between keeping your system cool and minimizing noise levels.
- To keep things quiet when using it just use speeds when it’s not doing higher speeds when there’s a lot to do.
- Ensure to swap out the paste
- Make sure to change the paste on your CPU or GPU every 2 to 4 years to keep the heat transferring between the parts and their heatsinks.
- Reasoning for Upgrading, to PWM Compatible Systems
With the development of cooling technology comes the opportunity to enhance performance and efficiency by switching to PWM systems, for improved reliability and overall effectiveness of your setup. Keep an eye out for these signs that may indicate it’s time, for an upgrade.

Conclusion
PWM cables play a role in today’s cooling solutions by providing control over fan speeds that can be adjusted dynamically as needed for optimal performance, in various settings such as gaming setups and industrial environments or everyday computer use while balancing cooling effectiveness, with energy efficiency and noise reduction through real-time temperature monitoring and adjustments enabled by transmitting PWM signals.
- What are the advantages of implementing PWM systems in contemporary cooling systems?
- Choosing PWM-controlled systems is a decision, for anyone looking to improve thermal regulation efficiency with advantages such, as
- Achieve performance by ensuring your hardware stays, at temperatures and efficiently utilizes energy resources.
- Experience reduced noise levels, for an atmosphere when there is less activity.
- Increase the longevity of fans by enhancing their efficiency, for use.
- PWM systems can seamlessly work with cooling configurations such, as cooling systems and fan control hubs, for enhanced flexibility and efficiency.
Contemporary tasks and robust hardware require cooling solutions in place, for the performance and longevity of your system setup. Switching to PWM systems represents a move that guarantees efficient operation with low noise levels and readiness, for future advancements. Regardless of whether you use your system for tasks or engage in gaming or professional workloads PWM technology provides superior performance suited to meet your specific requirements.

FAQs
What sets apart PWM fans, from PWM fans when it comes to controlling speed?
PWM fans utilize Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) which enables control over speed adjustments; in contrast, to PWM fans operate using voltage-based mechanisms to manage their speed levels.
What is the reason that PWM cables do not work with 5-pin PWM connectors?
PWM cables are made specifically for 4-pin connectors; however a 5-pin PWM connector has a pin arrangement and functions differently, than standard PWM cables hence making them incompatible, with each other.
What benefits do PWM fans offer compared to PWM fans?
PWM fans enable control of speed which leads to increased energy efficiency and quieter operation while enhancing cooling performance.
How does a 3-pin fan behave when connected to a PWM header?
The 3-pin fan will function but without PWM control. It will run at a default speed determined by the voltage provided by the header.
Why does a 3-pin connector not allow dynamic fan speed regulation based on system requirements?
A 3-pin connector lacks the dedicated PWM signal pin necessary for dynamic speed adjustments. Consequently, the fan operates at a fixed speed depending on the voltage supplied.

