When you overclock a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) you’re essentially pushing its clock speed and memory frequency beyond the settings to enhance its performance level, for frame rates during gaming or quicker rendering, in graphics heavy tasks.
Boosted Efficiency. By ramp, up the speed of the GPU unit in your system setup to unleash performance capabilities from your hardware device when handling resource intensive activities such, as gaming or video editing tasks. Enhanced Performance Potential; Boosting the performance through overclocking can enhance the capabilities of a mid range GPU to align closely with higher tier models and possibly prolong its usage duration.
When you overclock your system beyond its limits, with increased speed capabilities that the hardware can’t handle properly it might cause crashes or freezes along with graphical distortions popping up from time, to time. When a device gets too hot from running at speeds, than usual. Surpasses the cooling systems limits to handle it effectively may result in thermal throttling or harm.

1. Identifying Overclocking Issues
Symptoms of Overclocking Problems
- Frequent Crashes or Freezes: System instability often manifests during graphically intensive tasks like gaming or rendering.
- Artifacts or Visual Glitches: You might see distortions like flickering, colored spots, or broken textures on the screen.
- Overheating: The GPU may reach dangerously high temperatures, often accompanied by noisy fans or thermal throttling.
- Reduced Performance: Overclocking doesn’t always mean better performance; unstable settings can cause lower frame rates or system slowdowns.
Confirming Overclocking Settings
To verify if your GPU is overclocked:
- Use monitoring tools like:
- MSI Afterburner: Displays GPU clock speeds, temperatures, and fan usage.
- GPU-Z: Provides detailed hardware and performance information.
- Check for abnormal increases in core clock or memory clock values compared to manufacturer specifications.
If problems persist, consider reverting to default settings or fine-tuning overclock parameters to restore stability.

2. Preparing to Stop Overclocking
Store Customized Overclock Settings
Many programs used for overclocking GPUs such, as MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X enable you to store profiles for access, to your overclock configurations whenever necessary.
Custom Settings, for Documents
Be sure to jot down or capture the default and customized clock speeds of your GPU along, with the memory frequencies and voltage settings for access, on.
Make sure to keep your drivers up, to date.
The significance of having outdated drivers is that they can result in performance issues that are not related to overclocking and may cause problems to be misinterpreted.
Ways to make updates
Make sure to utilize software such, as NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Adrenalin to verify and update your drivers to the recent versions. For updates, on your GPU drivers instead; you can also check out the website of your GPU manufacturer.
- Make sure to look out for software that can overclock your system.
- Find out the software used to overclock.
People often rely upon tools such, as MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X to tweak their overclock settings easily and effectively. Please launch the software to confirm and make any changes, to the overclock settings that have been applied.
By following these steps outlined here you can make sure that troubleshooting runs smoothly and you can keep your GPUs performance and stability, in check.
3. Disabling Overclocking Through Software
Exploring the Potential of GPU Overclocking Software
Start the program by opening the tool you typically use to optimize performance settings on your computer—like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X.
- Go back, to the settings by choosing the option to reset to default or revert to the factory configuration.
- Remember to save the settings and then restart your system to make sure they are applied correctly.
Utilizing tools provided by the manufacturer.
Access GPU Utilities, by utilizing the software offered by your GPU manufacturer such, as NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Radeon Software.
Resetting Clock Speeds; Search, for a setting that allows you to revert the GPU clock speeds back, to their configurations usually found in the performance or tuning menus.
- Make sure to double check the action to guarantee that your GPU is running on its default settings.
- Here are some tips to help stabilize your GPU in case you encounter problems while overclocking it.
4. Disabling Overclocking Through BIOS/UEFI

When it comes to GPUs that support BIOS overclocking
To access the BIOS or UEFI settings, on your computer at startup simply press the specified key (such, as F12 or Delete).
Locate GPU Settings; Search for options related to GPU or performance in the menu.
- Resetting or turning off overclocking means restoring the settings or manually switching off the overclocking feature.
- Remember to save your work and then restart your computer before exiting the system.
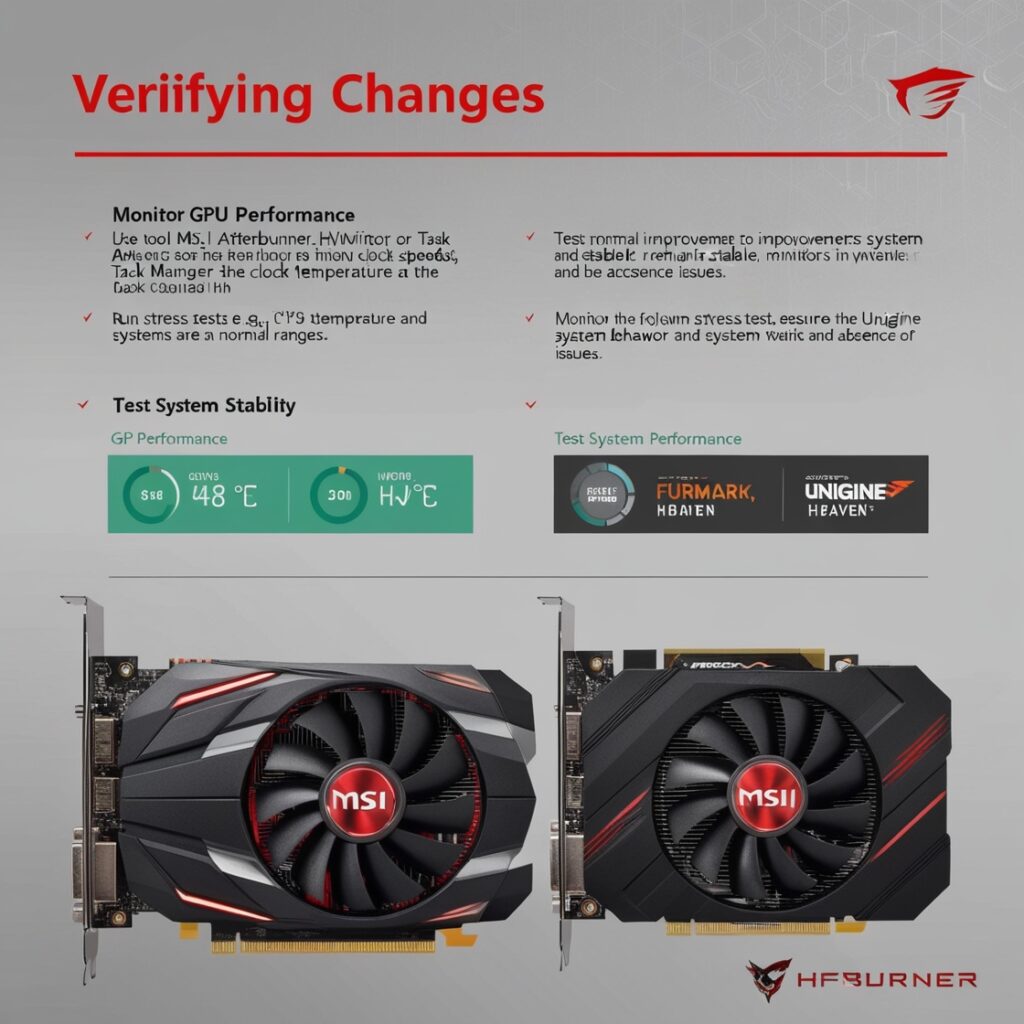
5. Verifying Changes
Keep an eye, on how your GPU’s performing.
Try using programs such, as MSI Afterburner or HW Monitor to monitor your GPUs performance metrics, like clock speeds and temperatures. Make sure that the values fall within the ranges recommended by the manufacturer.
Checking the stability of the system.
- Try conducting stress assessments, like Fur Mark or Unigine Heaven to assess how well the system performs when its put to the test, under loads.
- Make sure the system is running smoothly without any crashes or issues, like strange visual errors.
- Check for enhancements, in how the system operates and verify that there are no problems.
6. Alternative Solutions if Issues Persist
Decrease the amount of work
Try adjusting the graphics settings within the game or scaling back on demanding tasks to lighten the GPUs workload. This helps to avoid overheating and decreases in performance.
Apply the paste again
- If the device keeps getting too hot for comforts sake you might want to think about putting paste, between the graphics card and the cooling fins.
- It might also be an idea to inspect the GPUs cooling system for any dust accumulation or inadequate cooling measures.
Get help, from a professional
- If issues continue to occur get in touch with a technician. Reach out to the customer support team of the GPU maker for assistance.
- This could assist in identifying problems, with the hardware or suggesting fixes.

7. Preventing Future Overclocking Issues
Make sure to follow practices when overclocking
Slightly raise the clock speeds step, by step testing the systems stability after each adjustment. Try not making adjustments as it can lead instability or harm your hardware.
Routine upkeep
- Remember to keep your PC in tip shape by dusting it focus on areas, like the GPU and cooling system to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your system.
- Make sure that your computer case has airflow to help maintain temperatures. Keep an eye, on the temperatures. How well everything is running.
- Utilize software such, as MSI Afterburner or HW Monitor to monitor the temperature and performance of your GPU while overclocking it.
8. Conclusion
If you notice that overclocking your GPU results in issues, like system crashes or overheating problems and graphical anomalies appearing on screen – it’s important to halt the process ! Pushing your hardware beyond its boundaries can lead to lasting harm. Actually degrade performance instead of enhancing it.
When it comes to overclocking your system for a performance boost it’s important to prioritize stability and safety above all else. This ensures that your system operates smoothly with crashes while also extending the lifespan of your components. Never sacrifice the reliability of your system just to gain some performance. If you encounter instability issues it’s best to switch to default settings and avoid putting your GPU and overall system at risk.



